DIVERSITY OF CHORDATES
| HOME | AVES |
MODULE 8: CLASS AVES
8.1. Module Objectives
At the end of this module the learner will be able to:
1.State the characteristics of the class Aves
2.State the Orders of the class Aves
3.Describe the characteristics of the members of the various orders of the class Aves
8.2. Introduction
Aves are one of the most successful vertebrates that evolved from dinosaurs during Mezozoic era.
Figure 1 An Ave- Fowl
8.3. Basic characteristics of Aves.
8.3.1. Temperature control
Aves are endothermic. They can control their internal temperature by generating heat internally.
8.3.2. Body anatomy
Aves have scales on legs. It is assumed that the scales are remnants of reptilian features.
The body of Aves are covered with feathers. Feathers are special structures that over the body of birds. Basically feathers are used for insulation( temperature regulation) and fight.
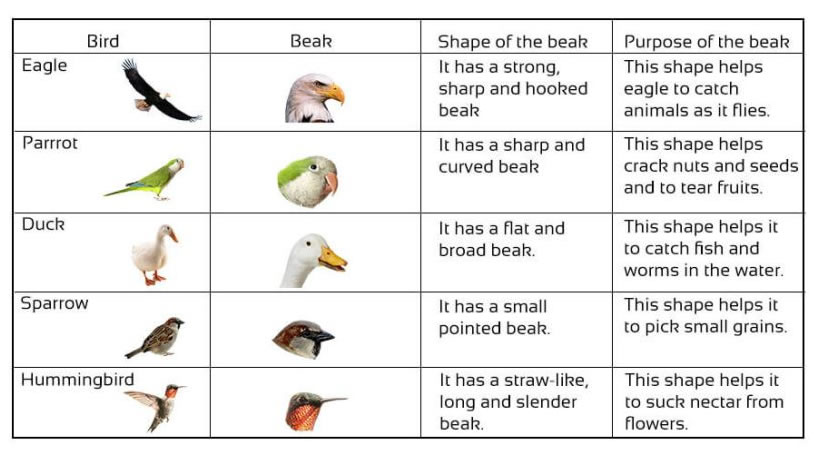
The feet of Birds have claws. While the mouth is modified into beaks. Beaks are made up of keratin. There are different types of beaks, modified to adapt to different feeding habits of the birds.
Birds lack some organs. For instance the females have one ovary only instead of two. Similarly, the Aves lack teeth. This makes the head to be lighter.
Figure 2 Feathers of Aves
The feet of Birds have claws. While the mouth is modified into beaks.
Figure 3 Beaks of birds
The forelimbs of Aves are modified into wings, used for flight.
Figure 4 Feat of birsds. Takshila Learning https://www.takshilalearning.com/cbse-class-3-evs-birds-and-their-features/ 1st January 2018
Figure 5 Modified wings of birds http://evolution-textbook.org/content/free/figures/ch03.html
Aves have light bones called pneumatic bones. This helps them to fly.
8.3.3. Reproduction
Reproduction in Aves takes place by separate sexes. Aves exhibits internal fertilization. After fertilization Birds produce the amniotic egg ( Hard-shelled eggs). Parental care. Birds take care of their young ones till they reached the maturity aged. This behavior called brooding. During brooding the parents feed and take care for their young.
Figure 6 Cleidoic/Shelled egg of Birds
8.3.4. Respiration
The respiratory system of births consists of tubes, air sacs. During respiration, air flows in only one direction. Gas exchange surfaces are constantly in contact with fresh air that contains a lot of oxygen. This enables birds to fly at high altitudes, where there is less oxygen in the atmosphere than at lower altitudes.
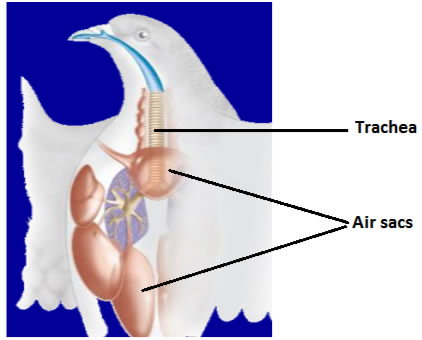
Figure 7 Respiratory system of \birds( Lungs and air sacs)
8.3.4. Circulatory system
Aves have efficient circulatory system comprising of four chambered heart, blood and blood vessel. They exhibit double blood circulatory system. A system whereby blood passes via the heart twice before transported to other organs of the body.
Figure 8 Heart of Aves- birds
8.3.5. Respiration
Aves have efficient control and coordinating system, comprising of strong nervous system, endocrine system, muscular system and sensory system. The brain is large and complex. They have efficient vision that enables them to navigate their environment efficiently and successfully.
Figure 9 Brain of birds
8.4. Modern Birds
The modern birds comprise of over 8600 species and 20 orders of birds. And they are classified into two groups namely:
8.4.1. Flightless birds. Example ostrich, emus, and kiwis.
8.4.2. Flying birds. Example The sparrow
8.4.1. Flightless birds
The flightless birds donot fly
Basic characteristics of flightless birds
Some of the basic characteristics of flightless birds are:
Flightless birds lack sternal keel on breastbone.
Flightless birds lack strong breast muscles needed for flight.
Figure10 Flightless bird (Ostrich)
8.4.2. Flying birds
The flying birds arethe group of birds that can be able to fly.
Basic characteristics of flying birds are
Some of the basic characteristics of flying birds are:
Flying birds possess a sternal keel on breastbone. Support strong breast muscles required for flight. Example is Sparrow
Figure 11 Flying birds
8.5. Characteristics the Aves share with Reptiles
Some of the characteristics the Aves share with reptiles are:
1.The Vertebral column.
2.Legs and feet covered by thick, dry scales.
3.Skin around beak is scaly.
4. Amniotic egg.
8.6. Adaptations for flight
Birds are the only animals that can fly. This attribute is as the result of the structural, physioloigcal and behavioural modification and adaptation of some of its structures/anatomy. Some of the features that lead to success of the birds in flyingare:
1.High metabolic raete (fast and effecient digestive process) to provide energy to fly.
2.Eat large amounts of food in proportion to body weight
3.Possess large eyes
4.Possess air sacs – increase amount of oxygen for respiration.
5.Rapid heart rate - muscles get more oxygen from blood.
6.Possess pneumonic bones (Hollow bones). Aids in the reduction in weight.
7.Powerful flight muscles attached to a keel.
8.7. Evolution of Aves
Aves are thought to have evolved from Reptiles some million years ago during the Mesozoic era. The closet dinosaur relative of the birds is called Theropods. Example: Velociraptor. This bird shows the features of both reptiles and birds.
8.8. Module summary
You have the following from this module:
1.The class Aves comprised of vertebrates whose bodies are covered with feathers.
2.Ave are ectoderms.
3.Aves exhibit external fertilization.
4.Aves produce amniotic egg
5.Aves have different types of beaks adapted for different diets or feeding habits.
6.Aves have pneumatic (hollow) bones.
7.Aves are divided into two groups, flightless Aves(Ostrich) and flying Aves( Sparrow).
| Reptiles | Mammals |
2019 Digital Vision Digital Resources