
| Home | NERVOUS SYSTEM | Log Out |
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
REFLEX ACTION
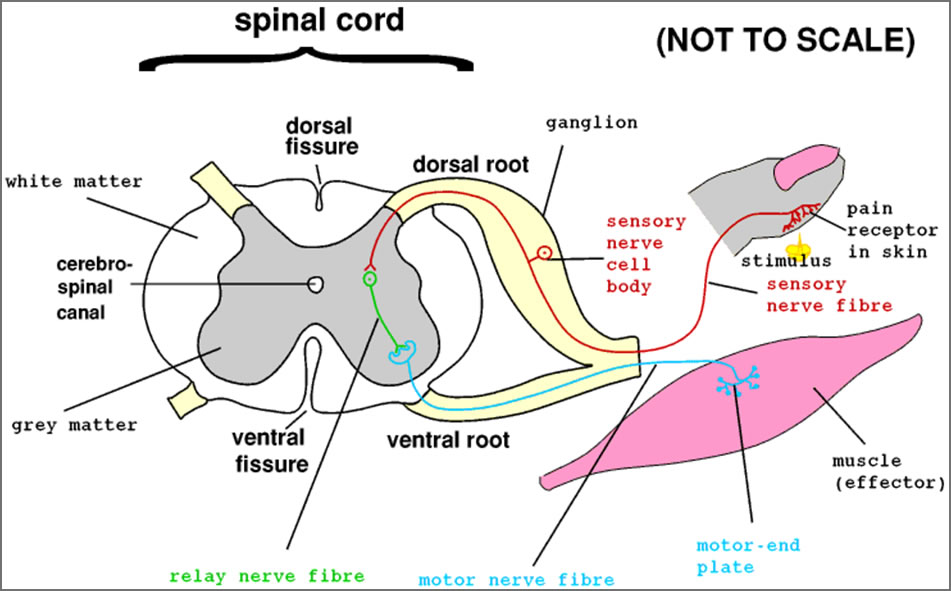
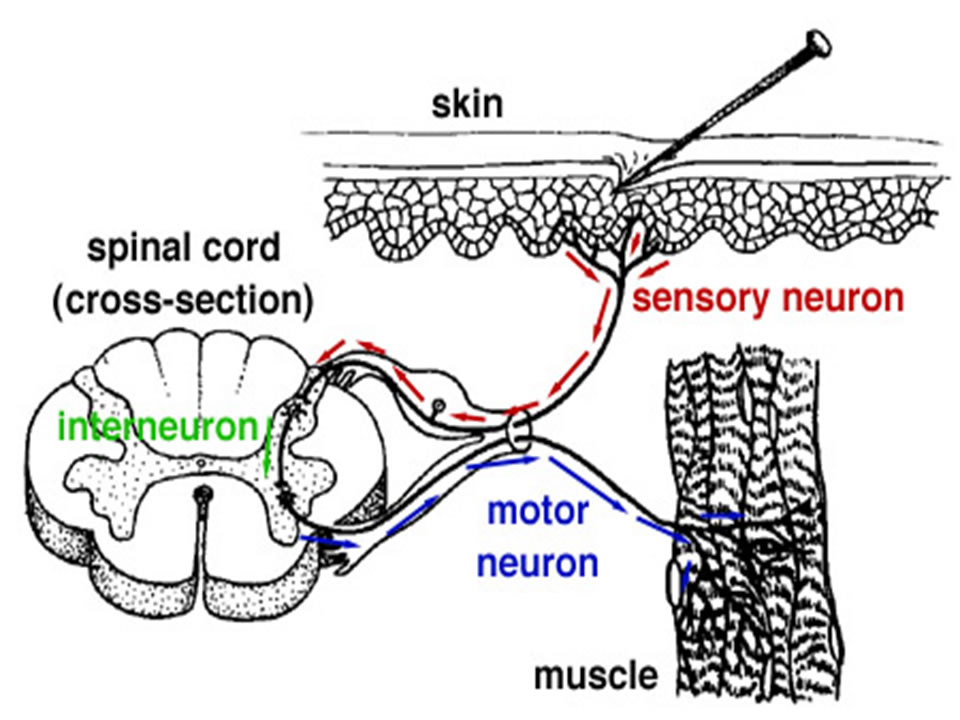
When you touch a hot object you automatically pull your hand away without a conscious effort. Such automatic reflex actions are governed by a simple combination of neurons called reflex arcs. Usually there are five (5) parts of a reflex arc (see text):
- Receptor - sense organ in skin, muscle, or other organ
- Sensory neuron - carries impulse towards CNS
- Interneuron - carries impulse within CNS
- Motor neuron - carries impulse away from CNS
- Effector - structure by which animal responds (muscle, gland, etc).
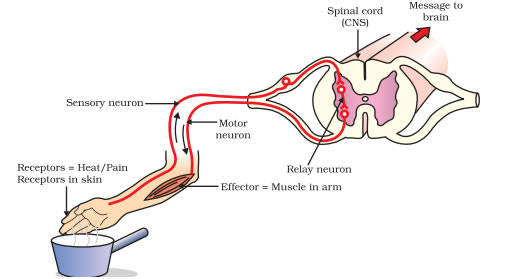
Reflex, or reflex action, is the involuntary movement of any organ or body part that has received a stimulus. It happens without any consciousness and is immediate. Reflexes protect the body from harm.
When we touch a hot bowl (here), the receptors present in our skin send an electrical impulse through neurons; via the sensory neuron it reaches the spinal cord and thus the message is sent to the brain.
The brain receives the signal while the reflex is being carried out. When reaching the relay neuron, it is transmitted through the motor neuron back to the effector that is the muscle.
The activation of the spinal motor neurons allows for a faster reaction time, hence the muscle moves to take the hand away from the hot object before instructions come back from the brain. This process together is called as reflex arc.
Thus we sense the heat and take our hand out of a body.
| How neurons work | Central nervous system |