
| Home | CIRCULATORY SYSTEM- BLOOD VESSELS |
1. Arteries
2. Veins
3. Capillaries
1. Arteries
Arteries are the blood vessels that transport oxygenated blood from the heart to other parts of the body (only pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood). They have thick walls. The largest artery that leaves the heart is the AORTA. The aorta splits into several arteries which terminate into different organs. The arteries terminate into smaller parts or region called arterioles.
Examples of arteries
-
Aorta- splits into ascending and descending arteries
-
Pulmonary artery
-
Right and left coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscles
-
Carotid artery carries blood to the head region
-
Hepatic artery carries blood to the liver
-
Renal artery carries blood to the kidneys
-
Iliac artery carries blood to the legs
-
Pulmonary artery- transport deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
The veins transport blood to the heart. They normally transport deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body to the lungs for oxygenation (with the exception of pulmonary veins). Veins have thin cell walls and large lumen (cavity). The lumen is lined up of with valves, which aid in preventing the reflux of blood into the organs. Examples of the veins are the superior and inferior vena cava. The veins terminate into smaller parts or region called venules.
Examples of veins
- Superior(anterior) vena cava- transports deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body to the lungs
- Inferior(posterior) vena cava- transports deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body to the lungs
- Pulmonary vein- transport oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
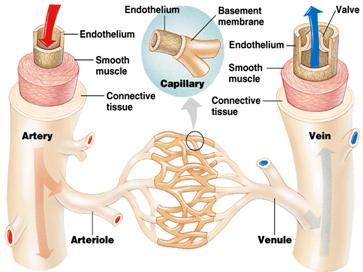
Figure Image of veins and arteries in man
The capillaries are the junctions or meeting points of the arteries and veins. Each vein terminates into venules, while each artery terminates into arteriole. The arteriole and the venule is connected via the capillaries. The capillaries are microscopic in nature and terminate in each organ of the body.
Functions of the capillaries
Some of the functions of the capillaries are:
- Transport of nutrients and other materials round the body
- Diffusion of materials to and from the body’s cells and the blood.
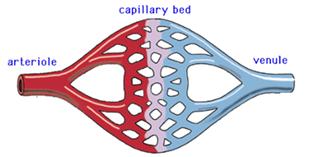
@iTutor 2003-2013. All rights reserved
Figure Image of the arteries, arterioles veins, venules and the capillaries
| PREV | NEXT |